If you want to ping a network device, which can only be done using the ICMP protocol, then you need a different library. I haven't tested the code and library on the following link (as I don't have a ethernetshield) but it should do what you want. The IP adress 74.125.26.147 in it replies when I ping it with Windows ping command. Internet speed tests, like this one or the test found at SpeedTest.net, measure the latter, or the speed reaching the device running the test. These test results are often lower than your plan speed due to various factors outside your Internet provider's control, including WiFi conditions and device capabilities.
Overview

This article provides helpful troubleshooting guidance for your Microsoft Azure StorSimple deployment. It describes common issues, possible causes, and recommended steps to help you resolve problems that you might experience when you configure StorSimple.
- Test your Internet line quality to locations around the world with this interactive ping test Pingtest Ookla is devoted to providing world-class products and services.
- At home one evening, Karsten Solheim putts with his first prototype putter head, and the tuning-fork-like construction makes a ‘ping’ sound when impacting the ball. Karsten excitedly runs into the kitchen and announces to his wife, Louise, “I’ve got a name for my putter!” Soon thereafter, he files for a patent on the PING 1-A putter.
- Start cmd /K sipp parameters1 ping -n 3 127.0.0.1 nul // pauses for 3 - 1 = 2 seconds total start cmd /K sipp parameters2 Enter Pjsua as a scripted call generator Pjsua sleep command allows to pipe commands from prepared text file to pjsua in a timely manner making it possible to use it as limited but very easy to use call generator.
This information applies to both the StorSimple 8000 series physical device and the StorSimple Cloud Appliance.
Note
Device configuration-related issues that you may face can occur when you deploy the device for the first time, or they can occur later, when the device is operational. This article focuses on troubleshooting first-time deployment issues. To troubleshoot an operational device, go to Use the Diagnostics tool to troubleshoot an operational device.
This article also describes the tools for troubleshooting StorSimple deployments and provides a step-by-step troubleshooting example.
First-time deployment issues
If you run into an issue when deploying your device for the first time, consider the following:
- If you are troubleshooting a physical device, make sure that the hardware has been installed and configured as described in Install your StorSimple 8100 device or Install your StorSimple 8600 device.
- Check prerequisites for deployment. Make sure that you have all the information described in the deployment configuration checklist.
- Review the StorSimple Release Notes to see if the problem is described. The release notes include workarounds for known installation problems.
During device deployment, the most common issues that users face occur when they run the setup wizard and when they register the device via Windows PowerShell for StorSimple. (You use Windows PowerShell for StorSimple to register and configure your StorSimple device. For more information on device registration, see Step 3: Configure and register your device through Windows PowerShell for StorSimple).
The following sections can help you resolve issues that you encounter when you configure the StorSimple device for the first time.
First-time setup wizard process
The following steps summarize the setup wizard process. For detailed setup information, see Deploy your on-premises StorSimple device.
Run the Invoke-HcsSetupWizard cmdlet to start the setup wizard that will guide you through the remaining steps.
Configure the network: the setup wizard lets you configure network settings for the DATA 0 network interface on your StorSimple device. These settings include the following:
- Virtual IP (VIP), subnet mask, and gateway – The Set-HcsNetInterface cmdlet is executed in the background. It configures the IP address, subnet mask, and gateway for the DATA 0 network interface on your StorSimple device.
- Primary DNS server – The Set-HcsDnsClientServerAddress cmdlet is executed in the background. It configures the DNS settings for your StorSimple solution.
- NTP server – The Set-HcsNtpClientServerAddress cmdlet is executed in the background. It configures the NTP server settings for your StorSimple solution.
- Optional web proxy – The Set-HcsWebProxy cmdlet is executed in the background. It sets and enables the web proxy configuration for your StorSimple solution.
Set up the password: the next step is to set up the device administrator password.The device administrator password is used to log on to your device. The default device password is Password1.
Important
Passwords are collected before registration, but applied only after you successfully register the device. If there is a failure to apply a password, you will be prompted to supply the password again until the required passwords (that meet the complexity requirements) are collected.
Register the device: the final step is to register the device with the StorSimple Device Manager service running in Microsoft Azure. The registration requires you to get the service registration key from the Azure portal, and provide it in the setup wizard. After the device is successfully registered, a service data encryption key is provided to you. Be sure to keep this encryption key in a safe location because it will be required to register all subsequent devices with the service.
Common errors during device deployment
The following tables list the common errors that you might encounter when you:
- Configure the required network settings.
- Configure the optional web proxy settings.
- Set up the device administrator password.
- Register the device.
Errors during the required network settings
| No. | Error message | Possible causes | Recommended action |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Invoke-HcsSetupWizard: This command can only be run on the active controller. | Configuration was being performed on the passive controller. | Run this command from the active controller. For more information, see Identify an active controller on your device. |
| 2 | Invoke-HcsSetupWizard: Device not ready. | There are issues with the network connectivity on DATA 0. | Check the physical network connectivity on DATA 0. |
| 3 | Invoke-HcsSetupWizard: There is an IP address conflict with another system on the network (Exception from HRESULT: 0x80070263). | The IP supplied for DATA 0 was already in use by another system. | Provide a new IP that is not in use. |
| 4 | Invoke-HcsSetupWizard: A cluster resource failed. (Exception from HRESULT: 0x800713AE). | Duplicate VIP. The supplied IP is already in use. | Provide a new IP that is not in use. |
| 5 | Invoke-HcsSetupWizard: Invalid IPv4 address. | The IP address is provided in an incorrect format. | Check the format and supply your IP address again. For more information, see Ipv4 Addressing. |
| 6 | Invoke-HcsSetupWizard: Invalid IPv6 address. | The IP address is provided in an incorrect format. | Check the format and supply your IP address again. For more information, see Ipv6 Addressing. |
| 7 | Invoke-HcsSetupWizard: There are no more endpoints available from the endpoint mapper. (Exception from HRESULT: 0x800706D9) | The cluster functionality is not working. | Contact Microsoft Support for next steps. |
Errors during the optional web proxy settings
| No. | Error message | Possible causes | Recommended action |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Invoke-HcsSetupWizard: Invalid parameter (Exception from HRESULT: 0x80070057) | One of the parameters provided for the proxy settings is not valid. | The URI is not provided in the correct format. Use the following format: http://<IP address or FQDN of the web proxy server>:<TCP port number> |
| 2 | Invoke-HcsSetupWizard: RPC server not available (Exception from HRESULT: 0x800706ba) | The root cause is one of the following:
| Depending on the root cause:
|
| 3 | Invoke-HcsSetupWizard: RPC call failed (Exception from HRESULT: 0x800706be) | Cluster is down. | Contact Microsoft Support to make sure that the cluster is up. |
| 4 | Invoke-HcsSetupWizard: Cluster resource not found (Exception from HRESULT: 0x8007138f) | The cluster resource is not found. This can happen when the installation was not correct. | You may need to reset the device to the factory default settings. Contact Microsoft Support to create a cluster resource. |
| 5 | Invoke-HcsSetupWizard: Cluster resource not online (Exception from HRESULT: 0x8007138c) | Cluster resources are not online. | Contact Microsoft Support for next steps. |
Errors related to device administrator password
The default device administrator password is Password1. This password expires after the first logon; therefore, you will need to use the setup wizard to change it. You must provide a new device administrator password when you register the device for the first time.
Make sure that your passwords meet the following requirements:
- Your device administrator password should be between 8 and 15 characters long.
- Passwords should contain 3 of the following 4 character types: lowercase, uppercase, numeric, and special.
- Your password cannot be the same as the last 24 passwords.
In addition, keep in mind that passwords expire every year, and can be changed only after you successfully register the device. If the registration fails for any reason, the passwords will not be changed.
For more information on device administrator password, go to Use the StorSimple Device Manager service to change your StorSimple password.
You may encounter one or more of the following errors when setting up the device administrator and StorSimple Snapshot Manager passwords.
| No. | Error message | Recommended action |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | The password exceeds the maximum length. | Your device administrator password must be between 8 and 15 characters long. |
| 2 | The password does not meet the required length. | Your device administrator password must be between 8 and 15 characters long. |
| 3 | The password must contain lowercase characters. | Passwords must contain 3 of the following 4 character types: lowercase, uppercase, numeric, and special. Make sure that your password meets these requirements. |
| 4 | The password must contain numeric characters. | Passwords must contain 3 of the following 4 character types: lowercase, uppercase, numeric, and special. Make sure that your password meets these requirements. |
| 5 | The password must contain special characters. | Passwords must contain 3 of the following 4 character types: lowercase, uppercase, numeric, and special. Make sure that your password meets these requirements. |
| 6 | The password must contain 3 of the following 4 character types: uppercase, lowercase, numeric, and special. | Your password does not contain the required types of characters. Make sure that your password meets these requirements. |
| 7 | Parameter does not match confirmation. | Make sure that your password meets all requirements and that you entered it correctly. |
| 8 | Your password cannot match the default. | The default password is Password1. You need to change this password after you log on for the first time. |
| 9 | The password you have entered does not match the device password. Please retype the password. | Check the password and type it again. |
Passwords are collected before the device is registered, but are applied only after successful registration. The password recovery workflow requires the device to be registered.
Important
In general, if an attempt to apply a password fails, then the software repeatedly attempts to collect the password until it is successful. In rare instances, the password cannot be applied. In this situation, you can register the device and proceed, however the passwords will not be changed. You can change the device administrator password after the registration from the Azure portal.
You can reset the password in the Azure portal via the StorSimple Device Manager service. For more information, go to Change the device administrator password.
Errors during device registration
You use the StorSimple Device Manager service running in Microsoft Azure to register the device. You could encounter one or more of the following issues during device registration.
| No. | Error message | Possible causes | Recommended action |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Error 350027: Failed to register the device with the StorSimple Device Manager. | Wait for a few minutes and then try the operation again. If the issue persists, contact Microsoft Support. | |
| 2 | Error 350013: An error has occurred in registering the device. This could be due to incorrect service registration key. | Please register the device again with the correct service registration key. For more information, see Get the service registration key. | |
| 3 | Error 350063: Authentication to StorSimple Device Manager service passed but registration failed. Please retry the operation after some time. | This error indicates that authentication with ACS has passed but the register call made to the service has failed. This could be a result of a sporadic network glitch. | If the issue persists, please contact Microsoft Support. |
| 4 | Error 350049: The service could not be reached during registration. | When the call is made to the service, a web exception is received. In some cases, this may get fixed by retrying the operation later. | Please check your IP address and DNS name and then retry the operation. If the problem persists, contact Microsoft Support. |
| 5 | Error 350031: The device has already been registered. | No action necessary. | |
| 6 | Error 350016: Device Registration failed. | Please make sure the registration key is correct. | |
| 7 | Invoke-HcsSetupWizard: An error has occurred while registering your device; this could be due to incorrect IP address or DNS name. Please check your network settings and try again. If the problem persists, contact Microsoft Support. (Error 350050) | Ensure that your device can ping the outside network. If you do not have connectivity to outside network, the registration may fail with this error. This error may be a combination of one or more of the following:
| See the steps in the Step-by-step troubleshooting example. |
| 8 | Invoke-HcsSetupWizard: The current operation failed due to an internal service error [0x1FBE2]. Please retry the operation after sometime. If the issue persists, please contact Microsoft Support. | This is a generic error thrown for all user invisible errors from service or agent. The most common reason may be that the ACS authentication has failed. A possible cause for the failure is that there are issues with the NTP server configuration and time on the device is not set correctly. | Correct the time (if there are issues) and then retry the registration operation. If you use the Set-HcsSystem -Timezone command to adjust the time zone, capitalize each word in the time zone (for example 'Pacific Standard Time'). If this issue persists, contact Microsoft Support for next steps. |
| 9 | Warning: Could not activate the device. Your device administrator and StorSimple Snapshot Manager passwords have not been changed. | If the registration fails, the device administrator and StorSimple Snapshot Manager passwords are not changed. |
Tools for troubleshooting StorSimple deployments
StorSimple includes several tools that you can use to troubleshoot your StorSimple solution. These include:
- Support packages and device logs.
- Cmdlets specifically designed for troubleshooting.
Support packages and device logs available for troubleshooting
A support package contains all the relevant logs that can assist the Microsoft Support team with troubleshooting device issues. You can use Windows PowerShell for StorSimple to generate an encrypted support package that you can then share with support personnel.
To view the logs or the contents of the support package
Use Windows PowerShell for StorSimple to generate a support package as described in Create and manage a support package.
Download the decryption script locally on your client computer.
Use this step-by-step procedure to open and decrypt the support package.
The decrypted support package logs are in etw/etvx format. You can perform the following steps to view these files in Windows Event Viewer:
Run the eventvwr command on your Windows client. This will start the Event Viewer.
In the Actions pane, click Open Saved Log and point to the log files in etvx/etw format (the support package). You can now view the file. After you open the file, you can right-click and save the file as text.
Important
You can also use the Get-WinEvent cmdlet to open these files in Windows PowerShell. For more information, see Get-WinEvent in the Windows PowerShell cmdlet reference documentation.
When the logs open in Event Viewer, look for the following logs that contain issues related to the device configuration:
- hcs_pfconfig/Operational Log
- hcs_pfconfig/Config
In the log files, search for strings related to the cmdlets called by the setup wizard. See First-time setup wizard process for a list of these cmdlets.
If you are not able to figure out the cause of the problem, you can contact Microsoft Support for next steps. Use the steps in Create a support request when you contact Microsoft Support for assistance.
Cmdlets available for troubleshooting
Use the following Windows PowerShell cmdlets to detect connectivity errors.
Get-NetAdapter: Use this cmdlet to detect the health of network interfaces.Test-Connection: Use this cmdlet to check the network connectivity inside and outside of the network.Test-HcsmConnection: Use this cmdlet to check the connectivity of a successfully registered device.Sync-HcsTime: Use this cmdlet to display device time and force a time sync with the NTP server.Enable-HcsPingandDisable-HcsPing: Use these cmdlets to allow the hosts to ping the network interfaces on your StorSimple device. By default, the StorSimple network interfaces do not respond to ping requests.Trace-HcsRoute: Use this cmdlet as a route tracing tool. It sends packets to each router on the way to a final destination over a period of time, and then computes results based on the packets returned from each hop. SinceTrace-HcsRouteshows the degree of packet loss at any given router or link, you can pinpoint which routers or links might be causing network problems.Get-HcsRoutingTable: Use this cmdlet to display the local IP routing table.
Troubleshoot with the Get-NetAdapter cmdlet
When you configure network interfaces for a first-time device deployment, the hardware status is not available in the StorSimple Device Manager service UI because the device is not yet registered with the service. Additionally, the Hardware health blade may not always correctly reflect the state of the device, especially if there are issues that affect service synchronization. In these situations, you can use the Get-NetAdapter cmdlet to determine the health and status of your network interfaces.
To see a list of all the network adapters on your device
Start Windows PowerShell for StorSimple, and then type
Get-NetAdapter.Use the output of the
Get-NetAdaptercmdlet and the following guidelines to understand the status of your network interface.- If the interface is healthy and enabled, the ifIndex status is shown as Up.
- If the interface is healthy but is not physically connected (by a network cable), the ifIndex is shown as Disabled.
- If the interface is healthy but not enabled, the ifIndex status is shown as NotPresent.
- If the interface does not exist, it does not appear in this list. The StorSimple Device Manager service UI will still show this interface in a failed state.
For more information on how to use this cmdlet, go to Get-NetAdapter in the Windows PowerShell cmdlet reference.
The following sections show samples of output from the Get-NetAdapter cmdlet.
In these samples, controller 0 was the passive controller, and was configured as follows:
- DATA 0, DATA 1, DATA 2, and DATA 3 network interfaces existed on the device.
- DATA 4 and DATA 5 network interface cards were not present; therefore, they are not listed in the output.
- DATA 0 was enabled.
Controller 1 was the active controller, and was configured as follows:
- DATA 0, DATA 1, DATA 2, DATA 3, DATA 4, and DATA 5 network interfaces existed on the device.
- DATA 0 was enabled.
Sample output – controller 0
The following is the output from controller 0 (the passive controller). DATA 1, DATA 2, and DATA 3 are not connected. DATA 4 and DATA 5 are not listed because they are not present on the device.
Sample output – controller 1
The following is the output from controller 1 (the active controller). Only the DATA 0 network interface on the device is configured and working.
Troubleshoot with the Test-Connection cmdlet
You can use the Test-Connection cmdlet to determine whether your StorSimple device can connect to the outside network. If all the networking parameters, including the DNS, are configured correctly in the setup wizard, you can use the Test-Connection cmdlet to ping a known address outside of the network, such as outlook.com.
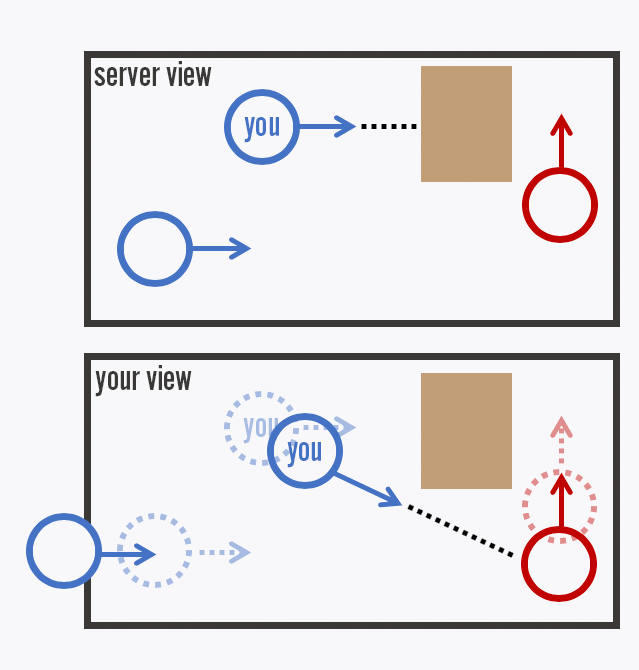
You should enable ping to troubleshoot connectivity issues with this cmdlet if ping is disabled.
See the following samples of output from the Test-Connection cmdlet.
Note
In the first sample, the device is configured with an incorrect DNS. In the second sample, the DNS is correct.
Sample output – incorrect DNS
In the following sample, there is no output for the IPV4 and IPV6 addresses, which indicates that the DNS is not resolved. This means that there is no connectivity to the outside network and a correct DNS needs to be supplied.
Sample output – correct DNS
In the following sample, the DNS returns the IPV4 address, indicating that the DNS is configured correctly. This confirms that there is connectivity to the outside network.
Troubleshoot with the Test-HcsmConnection cmdlet
Use the Test-HcsmConnection cmdlet for a device that is already connected to and registered with your StorSimple Device Manager service. This cmdlet helps you verify the connectivity between a registered device and the corresponding StorSimple Device Manager service. You can run this command on Windows PowerShell for StorSimple.
To run the Test-HcsmConnection cmdlet
Make sure that the device is registered.
Check the device status. If the device is deactivated, in maintenance mode, or offline, you might see one of the following errors:
- ErrorCode.CiSDeviceDecommissioned – this indicates that the device is deactivated.
- ErrorCode.DeviceNotReady – this indicates that the device is in maintenance mode.
- ErrorCode.DeviceNotReady – this indicates that the device is not online.
Verify that the StorSimple Device Manager service is running (use the Get-ClusterResource cmdlet). If the service is not running, you might see the following errors:
- ErrorCode.CiSApplianceAgentNotOnline
- ErrorCode.CisPowershellScriptHcsError – this indicates that there was an exception when you ran Get-ClusterResource.
Check the Access Control Service (ACS) token. If it throws a web exception, it might be the result of a gateway problem, a missing proxy authentication, an incorrect DNS, or an authentication failure. You might see the following errors:
ErrorCode.CiSApplianceGateway – this indicates an HttpStatusCode.BadGateway exception: the name resolver service could not resolve the host name.
ErrorCode.CiSApplianceProxy – this indicates an HttpStatusCode.ProxyAuthenticationRequired exception (HTTP status code 407): the client could not authenticate with the proxy server.
ErrorCode.CiSApplianceDNSError – this indicates a WebExceptionStatus.NameResolutionFailure exception: the name resolver service could not resolve the host name.
ErrorCode.CiSApplianceACSError – this indicates that the service returned an authentication error, but there is connectivity.
If it does not throw a web exception, check for ErrorCode.CiSApplianceFailure. This indicates that the appliance failed.
Check the cloud service connectivity. If the service throws a web exception, you might see the following errors:
ErrorCode.CiSApplianceGateway – this indicates an HttpStatusCode.BadGateway exception: an intermediate proxy server received a bad request from another proxy or from the original server.
ErrorCode.CiSApplianceProxy – this indicates an HttpStatusCode.ProxyAuthenticationRequired exception (HTTP status code 407): the client could not authenticate with the proxy server.
ErrorCode.CiSApplianceDNSError – this indicates a WebExceptionStatus.NameResolutionFailure exception: the name resolver service could not resolve the host name.
ErrorCode.CiSApplianceACSError – this indicates that the service returned an authentication error, but there is connectivity.
If it does not throw a web exception, check for ErrorCode.CiSApplianceSaasServiceError. This indicates a problem with the StorSimple Device Manager service.
Check Azure Service Bus connectivity. ErrorCode.CiSApplianceServiceBusError indicates that the device cannot connect to the Service Bus.
The log files CiSCommandletLog0Curr.errlog and CiSAgentsvc0Curr.errlog will have more information, such as exception details.
For more information about how to use the cmdlet, go to Test-HcsmConnection in the Windows PowerShell reference documentation.
Important
You can run this cmdlet for both the active and the passive controller.
See the following samples of output from the Test-HcsmConnection cmdlet.
Sample output – successfully registered device running StorSimple Update 3
Sample output – offline device
This sample is from a device that has a status of Offline in the Azure portal.
The device could not connect using the current web proxy configuration. This could be an issue with the web proxy configuration or a network connectivity problem. In this case, you should make sure that your web proxy settings are correct and your web proxy servers are online and reachable.
Troubleshoot with the Sync-HcsTime cmdlet
Use this cmdlet to display the device time. If the device time has an offset with the NTP server, you can then use this cmdlet to force-synchronize the time with your NTP server.
- If the offset between the device and NTP server is greater than 5 minutes, you will see a warning.
- If the offset exceeds 15 minutes, then the device will go offline. You can still use this cmdlet to force a time sync.
- However, if the offset exceeds 15 hours, then you will not be able to force-sync the time and an error message will be shown.
Sample output – forced time sync using Sync-HcsTime
Troubleshoot with the Enable-HcsPing and Disable-HcsPing cmdlets
Use these cmdlets to ensure that the network interfaces on your device respond to ICMP ping requests. By default, the StorSimple network interfaces do not respond to ping requests. Using this cmdlet is the easiest way to know if your device is online and reachable.
Sample output – Enable-HcsPing and Disable-HcsPing
Ping Registration Numbers
Troubleshoot with the Trace-HcsRoute cmdlet
Use this cmdlet as a route tracing tool. It sends packets to each router on the way to a final destination over a period of time, and then computes results based on the packets returned from each hop. Because the cmdlet shows the degree of packet loss at any given router or link, you can pinpoint which routers or links might be causing network problems.
Sample output showing how to trace the route of a packet with Trace-HcsRoute
Troubleshoot with the Get-HcsRoutingTable cmdlet
Use this cmdlet to view the routing table for your StorSimple device. A routing table is a set of rules that can help determine where data packets traveling over an Internet Protocol (IP) network will be directed.
The routing table shows the interfaces and the gateway that routes the data to the specified networks. It also gives the routing metric which is the decision maker for the path taken to reach a particular destination. The lower the routing metric, the higher the preference.
For example, if you have 2 network interfaces, DATA 2 and DATA 3, connected to the Internet. If the routing metrics for DATA 2 and DATA 3 are 15 and 261 respectively, then DATA 2 with the lower routing metric is the preferred interface used to reach the Internet.
If you are running Update 1 on your StorSimple device, your DATA 0 network interface has the highest preference for the cloud traffic. This implies that even if there are other cloud-enabled interfaces, the cloud traffic would be routed through DATA 0.
If you run the Get-HcsRoutingTable cmdlet without specifying any parameters (as the following example shows), the cmdlet will output both IPv4 and IPv6 routing tables. Alternatively, you can specify Get-HcsRoutingTable -IPv4 or Get-HcsRoutingTable -IPv6 to get a relevant routing table.
Step-by-step StorSimple troubleshooting example
The following example shows step-by-step troubleshooting of a StorSimple deployment. In the example scenario, device registration fails with an error message indicating that the network settings or the DNS name is incorrect.
The error message returned is:
The error could be caused by any of the following:
- Incorrect hardware installation
- Faulty network interface(s)
- Incorrect IP address, subnet mask, gateway, primary DNS server, or web proxy
- Incorrect registration key
- Incorrect firewall settings
To locate and fix the device registration problem
Check your device configuration: on the active controller, run
Invoke-HcsSetupWizard.Note
The setup wizard must run on the active controller. To verify that you are connected to the active controller, look at the banner presented in the serial console. The banner indicates whether you are connected to controller 0 or controller 1, and whether the controller is active or passive. For more information, go to Identify an active controller on your device.
Make sure that the device is cabled correctly: check the network cabling on the device back plane. The cabling is specific to the device model. For more information, go to Install your StorSimple 8100 device or Install your StorSimple 8600 device.
Note
If you are using 10 GbE network ports, you will need to use the provided QSFP-SFP adapters and SFP cables. For more information, see the list of cables, switches, and transceivers recommended for the 10 GbE ports.
Verify the health of the network interface:
- Use the Get-NetAdapter cmdlet to detect the health of the network interfaces for DATA 0.
- If the link isn't functioning, the ifindex status will indicate that the interface is down. You will then need to check the network connection of the port to the appliance and to the switch. You will also need to rule out bad cables.
- If you suspect that the DATA 0 port on the active controller has failed, you can confirm this by connecting to the DATA 0 port on controller 1. To confirm this, disconnect the network cable from the back of the device from controller 0, connect the cable to controller 1, and then run the Get-NetAdapter cmdlet again.If the DATA 0 port on a controller fails, contact Microsoft Support for next steps. You might need to replace the controller on your system.
Verify the connectivity to the switch:
- Make sure that DATA 0 network interfaces on controller 0 and controller 1 in your primary enclosure are on the same subnet.
- Check the hub or router. Typically, you should connect both controllers to the same hub or router.
- Make sure that the switches you use for the connection have DATA 0 for both controllers in the same vLAN.
Eliminate any user errors:
Run the setup wizard again (run Invoke-HcsSetupWizard), and enter the values again to make sure that there are no errors.
Verify the registration key used. The same registration key can be used to connect multiple devices to a StorSimple Device Manager service. Use the procedure in Get the service registration key to ensure that you are using the correct registration key.
Important
If you have multiple services running, you will need to ensure that the registration key for the appropriate service is used to register the device. If you have registered a device with the wrong StorSimple Device Manager service, you will need to contact Microsoft Support for next steps. You may have to perform a factory reset of the device (which could result in data loss) to then connect it to the intended service.
Use the Test-Connection cmdlet to verify that you have connectivity to the outside network. For more information, go to Troubleshoot with the Test-Connection cmdlet.
Check for firewall interference. If you have verified that the virtual IP (VIP), subnet, gateway, and DNS settings are all correct, and you still see connectivity issues, then it is possible that your firewall is blocking communication between your device and the outside network. You need to ensure that ports 80 and 443 are available on your StorSimple device for outbound communication. For more information, see Networking requirements for your StorSimple device.
Look at the logs. Go to Support packages and device logs available for troubleshooting.
If the preceding steps do not solve the problem, contact Microsoft Support for assistance.
Next steps
Learn how to use the Diagnostics tool to troubleshoot a StorSimple device.
Here you can find all secret codes for NOKIA 6.1 Plus. Check out how to enter hidden mode and use advanced options of Android 8.1 Oreo. Let's get access to secret information about NOKIA 6.1 Plus. Click here and find out more information about secret codes.
1. Phone information
*#*#4636#*#*
2. IMEI Info
*#06#
3. Calendar
*#*#225#*#*

4. FCM Diagnostics
*#*#426#*#*
5. Service Mode
*#*#372733#*#*
1. By typing '*#*#4636#*#*' you will be redirected to phone information menu. From that mode you can check Usage Statistics, Wi-Fi information and information about your NOKIA 6.1 Plus.
1.1 Phone Information - Here you can check your IMEI number, Signal strenght, cellinfo and connection type. Also you can run Ping test too.
1.2 Usage statistics - This one shows last time using App and usage time of it.
1.3 WiFi Information:
- Wi-Fi API - Here you can disable current WiFi network, disconnect connection, get information about connection and other stuff.
- Wi-Fi Configuration - On this page you can check information about connected network
- Wi-Fi Status - Read about connected network and run Ping test
2. Type in '*#06#' to see you IMEI number. IMEI is a International Mobile Equipment Identity number which you can use to identify your device. By using this code you can find specification of your device. Just go to https://www.imei.infoenter your number and check it.
3. Open phone dialer and enter *#*#225#*#*to see the Calendar. Here you will see all your events like birthday, anniversary, etc. .
4. FCM Diagnostics *#*#426#*#*
Ping Tester Registration Codes
5. To enable Service Mode you need to type in *#*#372733#*#*. In this menu you can how works modules in your phone like Camera,Speaker and more and more.
Registration Code Fifa 09
Articles
Google Ping Tester
Articles
Ping Tester Registration Code Finder
Check other NOKIA device solutions:
